In geometry, 3D shapes are solid shapes or figures that have three dimensions. Generally, length, width and height are the dimensions of 3D shapes (three-dimensional shapes). The common names of these shapes are cube, cuboid, cone, cylinder and sphere. 3D shapes are defined by their respective properties such as edges, faces, vertices, curved surfaces, lateral surfaces and volume.
We come across a number of objects of different shapes and sizes in our day-to-day life. There are golf balls, doormats, ice-cream cones, coke cans, and so on. In this article, we will discuss the various 3D shapes, surface area and volumes, and the process of making 3D shapes using nets with the help of 2D Shapes.
What are 3D Shapes?
In Geometry, 3D shapes are known as three-dimensional shapes or solids. 3D shapes have three different measures such as length, width, and height as its dimensions. The only difference between 2D shape and 3D shapes is that 2D shapes do not have a thickness or depth.
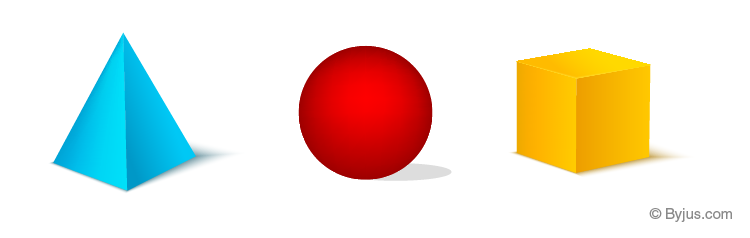
Usually, 3D shapes are obtained from the rotation of the 2D shapes. The faces of the solid shapes are the 2D shapes. Some examples of the 3D shapes are a cube, cuboid, cone, cylinder, sphere, prism and so on.
Types of 3D Shapes
The 3D shapes consist of both curved shaped solid and the straight-sided polygon called the polyhedron. The polyhedrons are also called the polyhedra, which are based on the 2D shapes with straight sides. Now, let us discuss the details about the polyhedrons and curved solids.
Polyhedrons
Polyhedrons are 3D shapes. As discussed earlier, polyhedra are straight-sided solids, which has the following properties:
- Polyhedrons should have straight edges.
- It should have flat sides are called the faces
- It must have the corners, called vertices
Like polygons in two-dimensional shapes, polyhedrons are also classified into regular and irregular polyhedrons and convex and concave polyhedrons.
The most common examples of polyhedra are:
- Cube: It has 6 square faces, 8 vertices and 12 edges
- Cuboid: It has 6 rectangular faces, 8 vertices and 12 edges
- Pyramid: It has a polygon base, straight edges, flat faces and one vertex
- Prism: It has identical polygon ends and flat parallelogram sides
Some other examples of regular polyhedrons are tetrahedrons, octahedrons, dodecahedrons, icosahedrons, and so on. These regular polyhedrons are also known as platonic solids, whose faces are identical to each face.
For example, the most commonly used example of a polyhedron is a cube, which has 6 faces, 8 vertices, and 12 edges.
Curved Solids
The 3D shapes that have curved surfaces are called curved solids. The examples of curved solids are:
- Sphere: It is a round shape, having all the points on the surface equidistant from center
- Cone: It has a circular base and a single vertex
- Cylinder: It has parallel circular bases, connected through curved surface
Faces Edges and Vertices
Faces, edges and vertices are three important measures of 3D shapes, that defines their properties.
- Faces – A face is a curve or flat surface on the 3D shapes
- Edges – An edge is a line segment between the faces
- Vertices – A vertex is a point where the two edges meet
Properties of 3D shapes
As we already discussed above the properties of 3D shapes are based on their faces, edges and vertices. Thus, we can have a brief of all the properties here in the table.
Surface Area and Volume of 3D shapes
The two different measures used for measuring the 3D shapes are:
- Surface Area
- Volume
Surface Area is defined as the total area of the surface of the two-dimensional object. The surface area is measured in terms of square units, and it is denoted as “SA”. The surface area can be classified into three different types. They are:
- Curved Surface Area (CSA) – Area of all the curved regions
- Lateral Surface Area (LSA) – Area of all the curved regions and all the flat surfaces excluding base areas
- Total Surface Area (TSA) – Area of all the surfaces including the base of a 3D object
Volume is defined as the total space occupied by the three-dimensional shape or solid. It is measured in terms of cubic units and it is denoted by “V”.
3D Shapes Formulas
The formulas of 3D shapes related to surface areas and volumes are:
3D Shapes Nets
A net is a flattened out three-dimensional solid. It is the basic skeleton outline in two dimensions, which can be folded and glued together to obtain the 3D structure. Nets are used for making 3D shapes. Let us have a look at nets for different solids and its surface area and volume formula.
Cuboid
A cuboid is also known as a rectangular prism. The faces of the cuboid are rectangular. All the angle measures are 90 degrees.
Take a matchbox. Cut along the edges and flatten out the box. This is the net for the cuboid. Now if you fold it back and glue it together similarly as you opened it, you get the cuboid.
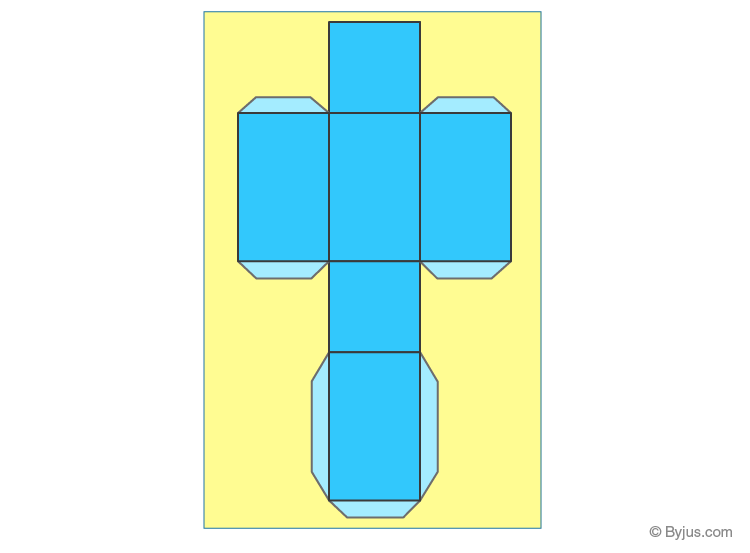
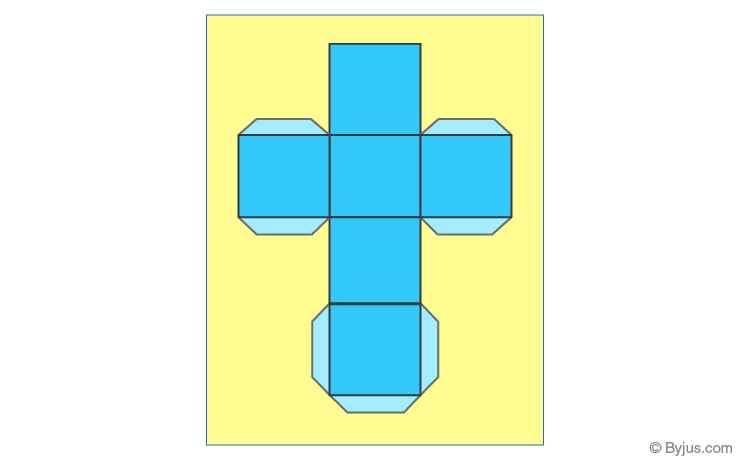
Cube
A cube is defined as a three-dimensional square with 6 equal sides. All the faces of the cube have equal dimension.
Take a cheese cube box and cut it out along the edges to make the net for a cube.
Cone
A cone is a solid object that has a circular base and has a single vertex. It is a geometrical shape that tapers smoothly from the circular flat base to a point called the apex.
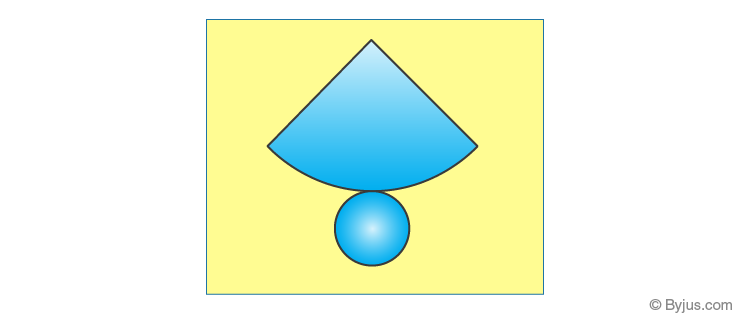
Take a birthday cap which is conical. When you cut a slit along its slant surface, you get a net for cone.
Cylinder
A cylinder is a solid geometrical figure, that has two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface.
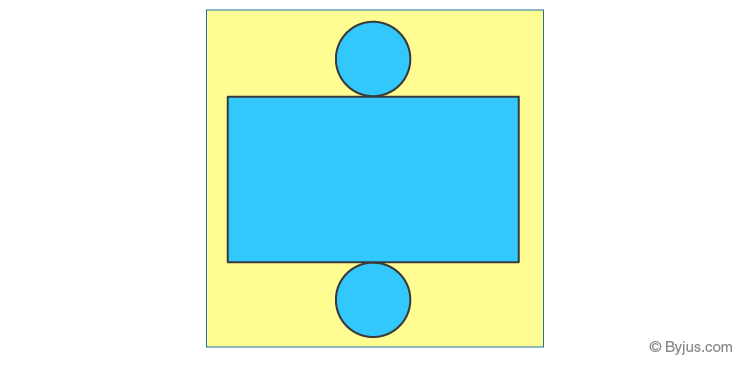
When you cut along the curved surface of any cylindrical jar, you get a net for the cylinder. The net consists of two circles for the base and the top and a rectangle for the curved surface.
Pyramid
A pyramid, also known as a polyhedron. A pyramid can be any polygon, such as a square, triangle and so on. It has three or more triangular faces that connect at a common point is called the apex.
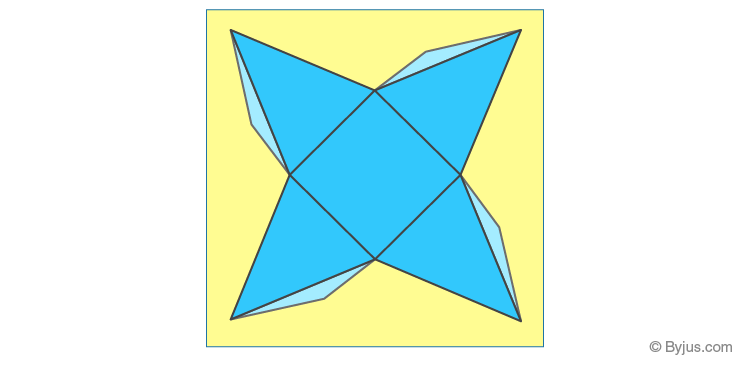
The net for a pyramid with a square base consists of a square with triangles along its four edges.
Solved Examples
Q.1: What is the surface area of a cube, if the edge length is 4 cm?
Solution: Given, the edge of cube = 4cm
By the formula we know that;
Surface area of a cube = 6a2 where a is the edge-length
SA = 6 (4)2 sq.cm
SA = 96 sq.cm
Q.2: Find the volume of cylinder if radius = 3cm and height = 7cm.
Solution: Given, the dimensions of cylinder are:
Radius = 3cm
Height = 7cm
Volume of cylinder = πr2h
= 22/7 x 32 x 7
= 198 cu.cm. (Approximate)








0 Comments