Trigonometry values of different ratios, such as sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cotangent, and cosecant, deal with the measurement of lengths and angles of the right-angle triangle. The values of trigonometric functions for 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90° are commonly used to solve trigonometry problems.
Trigonometry values are all about the study of standard angles for a given triangle with respect to trigonometric ratios. The word ‘trigon’ means triangle and ‘metron’ means ‘measurement’. It’s one of the major concepts and part of geometry, where the relationship between angles and sides of a triangle is explained.
Maths is an important subject, where we learn about different types of calculations and logic applied in our day-to-day life. Trigonometry basics are widely explained in students’ academic classes 9 and 10. Here, you will learn about different trigonometric ratios and formulas. Also, solve problems based on these formulas and identities to understand the fundamentals of trigonometry in a better way.
Trigonometry Values Table
Let us learn, trigonometry values for angles 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°, with respect to sin, cos, tan, cot, sec, cosec functions, taking an example of the right-angle triangle.
Suppose ABC is a right-angled triangle, right-angled at B. This triangle has a hypotenuse AC, an adjacent side AB which is adjacent to ∠θ and a perpendicular BC opposite to ∠θ.
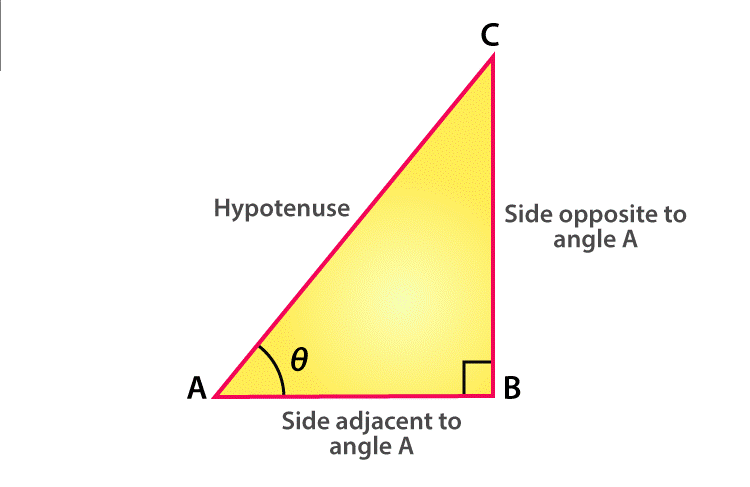
Trigonometry values are based on three major trigonometric ratios, Sine, Cosine, and Tangent.
- Sine or sin θ = Side opposite to θ / Hypotenuse = BC / AC
- Cosines or cos θ = Adjacent side to θ / Hypotenuse = AB / AC
- Tangent or tan θ =Side opposite to θ / Adjacent side to θ = BC / AB
Similarly, we can write the trigonometric values for Reciprocal properties, Sec, Cosec and Cot ratios.
- Sec θ = 1/Cos θ = Hypotenuse / Adjacent side to angle θ = AC / AB
- Cosec θ = 1/Sin θ = Hypotenuse / Side opposite to angle θ = AC / BC
- Cot θ = 1/tan θ = Adjacent side to angle θ / Side opposite to angle θ = AB / BC
Also,
- Sec θ . Cos θ =1
- Cosec θ . Sin θ =1
- Cot θ . Tan θ =1
Trigonometry Ratios Formula
- Tan θ = sin θ/cos θ
- Cot θ = cos θ/sin θ
- Sin θ = 1/cosec θ
- Cos θ = sin θ/tan θ = 1/sec θ
- Sec θ = tan θ/sin θ = 1/cos θ
- Cosec θ = 1/sin θ
Also,
- Sin (90°-θ) = Cos θ
- Cos (90°-θ) = Sin θ
- Tan (90°-θ) = Cot θ
- Cot (90°-θ) = Tan θ
- Sec (90°-θ) = Cosec θ
- Cosec (90°-θ) = Sec θ
Trigonometry Examples
Example 1:
Find the value of sin(90 – 45)°.
Solution:
sin(90 – 45)° = cos 45° = 1/√2
Example 2:
If tan θ = 4 and sin θ = 6. Then find the value of cos θ.
Solution:
We know, cos θ = sin θ/ tan θ
Therefore, cos θ = 6/4 = 3/2








0 Comments