Plants are one of the most essential living organisms on earth. They are immensely beneficial to both animals and human beings. They produce oxygen which is crucial for the survival of living organisms. Trees provide shelter to animals and are also known for their medicinal benefits. Overall, different parts of plants have different roles to perform. They act as a source of food and oxygen and maintain the ecological balance.
A plant has many parts. Different parts perform different functionalities. The part of the plant that appears above the ground level is called the shoot system while the part of the plant which lies underneath the soil is called the root system.
For better understanding, we need to know in detail about the different parts of plants and their functions. Let’s have a glance at the structure of different plant parts and how they are beneficial to the environment.
Parts Of Plants
The main parts of a plant include:
- Roots
- Stem
- Leaves
- Flowers
- Fruits
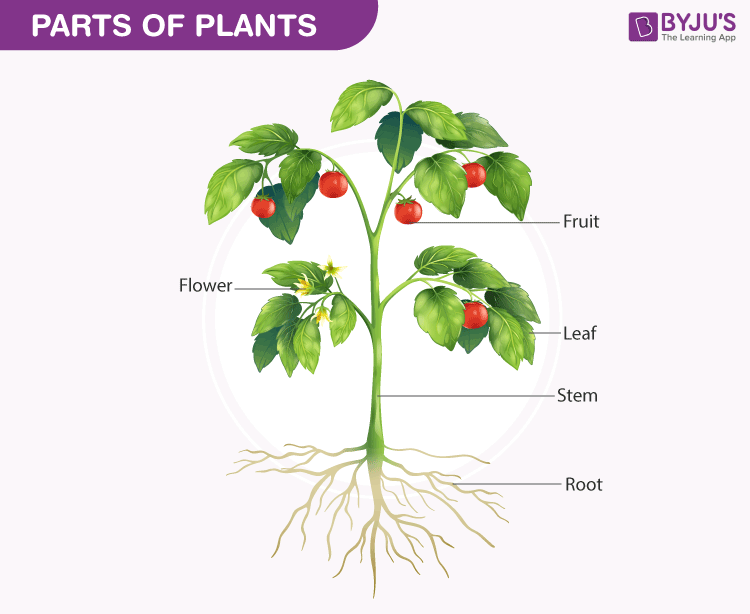
Parts Of Plants Diagram
Roots
Roots are the most important and underground part of a plant, which are collectively called the root system. They are the major part that anchors the plant firmly in the soil. They absorb water and minerals from the soil, synthesise plant growth regulators, and store reserve food material. The apical part of the root is covered by the root cap that protects the root apex.
The direct elongation of radicle leads to the formation of primary roots that grow inside the soil in dicots. It bears lateral roots that are known as secondary and tertiary roots.
In monocots, the primary root is replaced by a large number of roots because it is short-lived. In some plants such as Banyan tree, the roots arise from the parts of the plant and not from the radical. Such roots are known as adventitious roots.
A few plants that grow in swampy areas have roots growing vertically upwards to get oxygen for respiration. Such roots are known as pneumatophores.
Stem
The stem is the part of the plant which is found above the ground. The bark of trees are brown in colour and younger stems are green in colour. It forms the basis of the shoot system and bears leaves, fruits and flowers. The region where the leaves arise is known as the node and the region between the nodes is known as the internode.
Stems arise from the plumule, vertically upwards to the ground. Initially, stems are usually weak and cannot stand straight. It eventually grows to become the toughest part of the plant called the trunk. The trunk is covered by a thick outer covering known as the bark. Overall stem provides a definite framework and structure to a plant, which later develops into a tree.
The stem provides support to the plant. They also protect the plant and help in vegetative propagation. A few underground stems such as potato and ginger are modified to store food.
The important functions of a stem include:
- A stem carries out a number of functions essential for various processes such as photosynthesis.
- Provides a definite framework and structure to a plant which later develops into a tree.
- Support: Primary function of the stem is to hold up buds, flowers, leaves, and fruits to the plant. Along with the roots, a stem anchors the plants and helps them to stand upright and perpendicular to the ground.
- Transportation: It is the part which transports water and minerals from the root and prepared food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
- Storage: Stems are one of the storerooms of plants where the prepared food is stored in the form of starch. The stems of a few plants in the desert areas, such as Opuntia, get modified into thick, fleshy structures that store food and prevent excessive water loss due to transpiration.
- Reproduction: A few stems help in reproduction through vegetative propagation and also help to bear flowers and to produce fruits.
- Guards: Protects Xylem and phloem allowing them to perform their functions. The stem tendrils are spirally coiled and help the plant to climb support. The axillary buds also get modified into thorns that protect the plant from grazing animals.
- The stems of a few plants in the desert areas, such as Opuntia, get modified into thick, fleshy structures that store food and prevent excessive water loss due to transpiration.
Leaves
Leaves are the most important part of a plant. They contain chlorophyll that helps the plants to prepare their food using sunlight, carbon dioxide and water. A leaf consists of three main parts- petiole, leaf base and lamina.
- The petiole keeps the leaf blade exposed to wind and cools the leaf.
- The leaf base is a protruding part of a leaf.
- The lamina of the leaf contains veins and veinlets that provide rigidity to the leaf blade and help in the transport of mineral nutrients.
Primarily, leaves have three main functions:
- Photosynthesis: Green leaves prepare food for plants by using water and carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight. This process is called photosynthesis.
- Transpiration: Other than photosynthesis, leaves play a crucial role in the removal of excess of water from plants through tiny pores called stomata. This is the process of transpiration.
- Reproduction: Leaves of some plants helps in reproduction also. For e.g. leaves of Bryophyllum give rise to a new Bryophyllum plant.

Leaf and its parts
Other Parts of Plants
The other parts of a plant include flowers and fruits.
Flowers
Flowers are the most beautiful and colourful part of a plant. They are the reproductive part of a plant. A flower has four major parts, namely,
- Petals: It is the colourful part of a flower which attracts insects and birds.
- Sepals: Sepals are green leafy parts present under petals and protect the flower buds from damage.
- Stamens: This is the male part of the flower consisting of anther and filament.
- Pistil: This is the female part of the flower consisting of stigma, style and ovary.
Fruits
Fruits are the main features of a flowering plant. It is a matured ovary that develops after fertilisation. Some fruits are developed without fertilization and are known as parthenocarpic fruits and the process is known as Parthenocarpy.
Thus, we see how different parts of a plant help in the growth and development of a plant. All the plant parts are beneficial and work in coordination with each other.








0 Comments