Carbohydrates are macronutrients and are one of the three main ways by which our body obtains its energy. They are called carbohydrates as they comprise carbon, hydrogen and oxygen at their chemical level. Carbohydrates are essential nutrients which include sugars, fibers and starches. They are found in grains, vegetables, fruits and in milk and other dairy products. They are the basic food groups which play an important role in a healthy life.
The food containing carbohydrates are converted into glucose or blood sugar during the process of digestion by the digestive system.
Our body utilizes this sugar as a source of energy for the cells, organs and tissues. The extra amount of energy or sugar is stored in our muscles and liver for further requirement. The term ‘carbohydrate’ is derived from a French term ‘hydrate de carbone‘ meaning ‘hydrate of carbon‘. The general formula of this class of organic compounds is Cn(H2O)n.
Classification of Carbohydrates
The carbohydrates are further classified into simple and complex which is mainly based on their chemical structure and degree of polymerization.
Simple Carbohydrates (Monosaccharides, Disaccharides and Oligosaccharides)
Simple carbohydrates have one or two sugar molecules. In simple carbohydrates, molecules are digested and converted quickly resulting in a rise in the blood sugar levels. They are abundantly found in milk products, beer, fruits, refined sugars, candies, etc. These carbohydrates are called empty calories, as they do not possess fiber, vitamins and minerals.
Plants, being producers, synthesize glucose (C6H12O6) using raw materials like carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight. This process of photosynthesis converts solar energy to chemical energy. Consumers feed on plants and harvest energy stored in the bonds of the compounds synthesized by plants.
Also, read more about Photosynthesis
1. Monosaccharides
Glucose is an example of a carbohydrate monomer or monosaccharide. Other examples of monosaccharides include mannose, galactose, fructose, etc. The structural organization of monosaccharides is as follows:
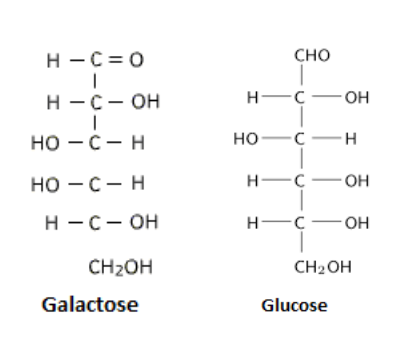
Monosaccharides may be further classified depending on the number of carbon atoms:
(i)Trioses (C3H6O3): These have three carbon atoms per molecule. Example: Glyceraldehyde
(ii)Tetroses (C4H6O4): These monosaccharides have four carbon atoms per molecule. Example: Erythrose.
Similarly, we have-
(iii) Pentoses,
(iv) Hexoses, and
(v) Heptoses
2. Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides combine to form a disaccharide. Examples of carbohydrates having two monomers include- Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose, etc.
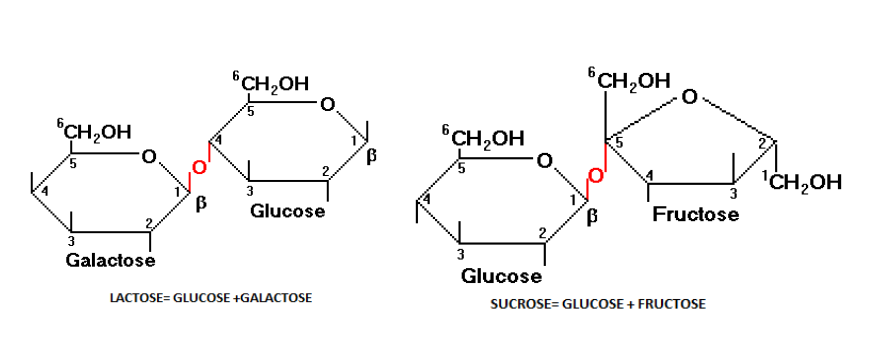
3. Oligosaccharides
Carbohydrates formed by the condensation of 2-9 monomers are called oligosaccharides. By this convention, trioses, pentoses, hexoses are all oligosaccharides.
Complex Carbohydrates (Polysaccharides)
Complex carbohydrates have two or more sugar molecules, hence they are referred to as starchy foods. In complex carbohydrates, molecules are digested and converted slowly compared to simple carbohydrates. They are abundantly found in lentils, beans, peanuts, potatoes, peas, corn, whole-grain bread, cereals, etc.
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates formed by the polymerization of a large number of monomers. Examples of polysaccharides include starch, glycogen, cellulose, etc. which exhibit extensive branching and are homopolymers – made up of only glucose units.
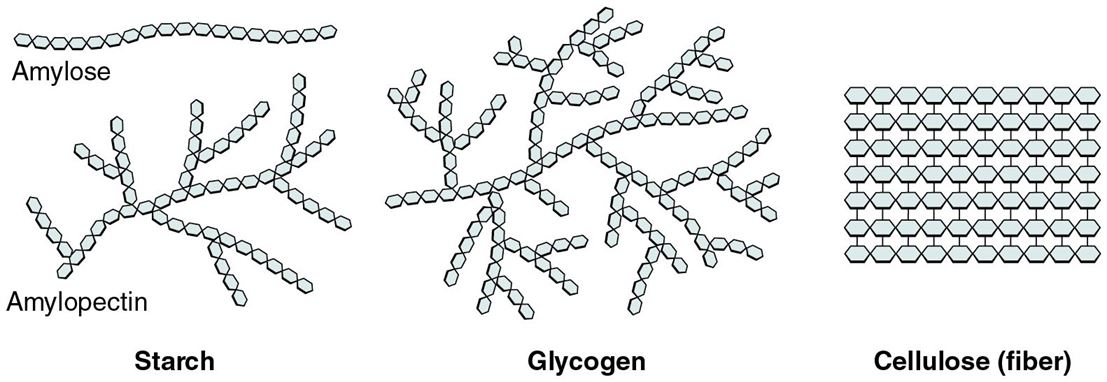
- Starch is composed of two components- amylose and amylopectin. Amylose forms the linear chain and amylopectin is a much-branched chain.
- Glycogen is called animal starch. It has a structure similar to starch, but has more extensive branching.
- Cellulose is a structural carbohydrate and is the main structural component of the plant cell wall. It is a fibrous polysaccharide with high tensile strength. In contrast to starch and glycogen, cellulose forms a linear polymer.
Functions of Carbohydrates
The main function of carbohydrates is to provide energy and food to the body and to the nervous system.
Carbohydrates are known as one of the basic components of food, including sugars, starch, and fibre which are abundantly found in grains, fruits and milk products.
Carbohydrates are also known as starch, simple sugars, complex carbohydrates and so on.
It is also involved in fat metabolism and prevents ketosis.
Inhibits the breakdown of proteins for energy as they are the primary source of energy.
An enzyme by name amylase assists in the breakdown of starch into glucose, finally to produce energy for metabolism.
Sources of Carbohydrates
- Simple sugars are found in the form of fructose in many fruits.
- Galactose is present in all dairy products.
- Lactose is abundantly found in milk and other dairy products.
- Maltose is present in cereal, beer, potatoes, processed cheese, pasta, etc.
- Sucrose is naturally obtained from sugar and honey containing small amounts of vitamins and minerals.
These simple sugars that consist of minerals and vitamins exist commonly in milk, fruits, and vegetables. Many refined and other processed foods like white flour, white rice, and sugar, lack important nutrients and hence, they are labelled “enriched.” It is quite healthy to use vitamins, carbohydrates and all other organic nutrients in their normal forms.
Carbohydrate Foods
Eating too much sugar results in an abnormal increase in calories, which finally leads to obesity and in turn low calories leads to malnutrition. Therefore, a well-balanced diet needs to be maintained to have a healthy life. That is the reason a balanced diet is stressed so much by dietitians.
Let us look into the differences between the good and bad carbohydrates.
Examples of Carbohydrates
Following are the important examples of carbohydrates:
- Glucose
- Galactose
- Maltose
- Fructose
- Sucrose
- Lactose
- Starch
- Cellulose
- Chitin








0 Comments