Force is required to make an object move, and force acts differently on objects depending on the type of motion it exhibits. In the case of curvilinear motion, a special force comes into the picture, i.e., centripetal force – literally meaning “centre seeking.” Centripetal force is the force acting towards the centre of the circular path. In this article, let us discuss what centripetal force is and how it is different from centrifugal force.
Defining Centripetal Force
According to the centripetal force definition,
Centripetal force is the force acting on an object in curvilinear motion directed towards the axis of rotation or centre of curvature.
The unit of centripetal force is newton.
The centripetal force is always directed perpendicular to the direction of the object’s displacement. Using Newton’s second law of motion, it is found that the centripetal force of an object moving in a circular path always acts towards the centre of the circle.
Calculating Centripetal Force
The Centripetal Force Formula is given as the product of mass (in kg) and tangential velocity (in meters per second) squared, divided by the radius (in meters) that implies that on doubling the tangential velocity, the centripetal force will be quadrupled. Mathematically it is written as:
Where, F is the Centripetal force, m is the mass of the object, v is the speed or velocity of the object and r is the radius.
Centripetal Force Examples in Daily Life
The centripetal force pulls or pushes an object towards the centre of a circle as it travels, causing angular or circular motion.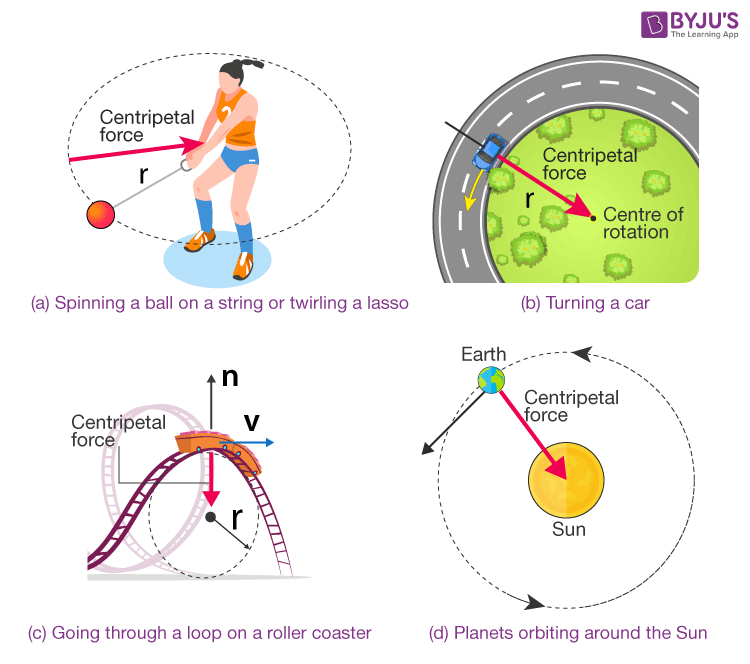
- When spinning a ball on a string or twirling a lasso, the force of tension on the rope pulls the object towards the centre.
- The centripetal force is provided by the frictional force between the ground and the wheels when turning a car.
- When going through a loop on a roller coaster, the force is provided by the normal force as the seat or wall pushes you towards the centre.
- For the planets orbiting around the Sun, the centripetal force is provided by Gravity.
What Is Centrifugal Force?
Centrifugal force is a pseudo force in a circular motion which acts along the radius and is directed away from the centre of the circle. The force does not exist when measurements are made in an inertial frame of reference. It only comes into play when changing our reference frame from a ground/inertial to a rotating reference frame.
The centrifugal force’s unit is newton.
Calculating Centrifugal Force
A centrifugal force basically uses the centripetal force formula (which describes a real phenomenon) and reverses the direction of the force, to describe the fictitious centrifugal force.
Where, F is the Centrifugal force, m is the mass of the object, v is the speed or velocity of the object and r is the radius.
Centrifugal Force Examples in Daily Life
Centrifugal Force acts on every object moving in a circular path when viewed from a rotating frame of reference. Some examples of Centrifugal Force are given below.
- Weight of an object at the poles and on the equator
- A bike making a turn.
- Vehicle driving around a curve
- Equatorial railway
Centripetal Force vs Centrifugal Force
Check the table below to learn the detailed comparison between Centripetal and Centrifugal Force








0 Comments