All living organisms are made up of a fundamental unit called the cell. Each cell is made up of organic as well as inorganic compounds. The elemental analysis of the cell constituents shows that a cell comprises carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus, etc. Proteins, Carbohydrates, Fats, and Nucleic acids are known as Biomolecules.
What are Biomolecules?
Biomolecules are defined as any organic molecule present in a living cell which includes carbohydrates, proteins, fats etc. Each biomolecule is essential for body functions and manufactured within the body. They can vary in nature, type, and structure where some may be straight chains, some may be cyclic rings or both. Also, they can vary in physical properties such as water solubility and melting points.
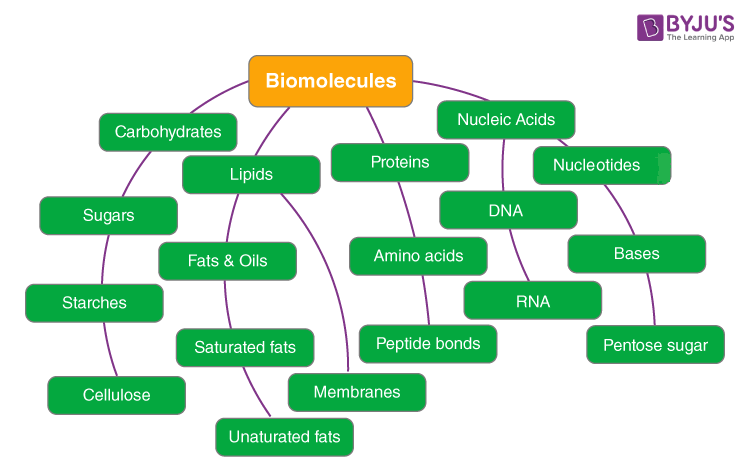
Types of Biomolecules
Biomolecules are primarily classified into 4 types, namely:
Carbohydrates
Polysaccharides, commonly known as carbohydrates are macromolecules. They are polymers made up of monosaccharide monomers (sugar molecules). The majority of living cells are rich in carbohydrates and they are the final products of many metabolic processes. For example, Glucose is the final product of photosynthesis. Carbohydrates can be monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides etc. based on the number of sugar molecules they are made up of.
Proteins
Proteins are polymers, made up of monomeric units of 20 amino acids. Amino acids are linked together in a specific sequence by peptide bonds to form long polypeptide chains. Amino acids are substituted methane, where a central C is linked to an amino group, carboxylic group, hydrogen and different R groups. R group varies in different amino acids. E.g. Glycine contains H as a side chain, Alanine has -CH3 as the R group, etc. Protein contains 20 amino acids, of which 11 are non-essential and 9 are essential, i.e. to be supplemented in the diet.
Lipids
Lipids are hydrophobic macromolecules. Lipids include fats, oils, wax, phospholipids, steroids, etc. Fatty acids are the most simple lipids, they contain carboxylic acids with a long-chain variable R group, which can be saturated or unsaturated. Fatty acids form triglycerides after combining with glycerol, which is trihydroxy propane. Phospholipids are the main constituents of the cell membrane. Phospholipids are made up of two hydrophobic fatty acid tails and a hydrophilic head consisting phosphate group.
Nucleic Acids
The genetic material present in all living organisms and viruses is DNA and RNA, which are nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a nitrogenous base, sugar and a terminal phosphate group. Nitrogenous bases are of two types: pyrimidines and purines. A base linked with sugar (deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA) is known as a nucleoside. Nucleoside joins a phosphate group to form nucleotides. These nucleotides are bonded together by phosphodiester linkage to form nucleic acids like DNA and RNA.
The human body consists of trillions of cells which are made up of carbohydrates, proteins and other biomolecules. The majority of cell activities depend on them.








0 Comments