Evolution is defined as the gradual process by which a simple life form leads to the development of complex organisms over a period of time, spanning several generations.
Charles Darwin
- Charles Darwin, also called the “Father of Evolution”, was an English Naturalist and Biologist.
- Five years of the expedition in a ship called HMS Beagle to Galapagos Island helped him write his theory of evolution.
- In 1859 he published a book called Origin of Species, in which he put his theory of evolution in detail.
Evolution and Fossils
Evolution
Evolution is a tangible change in the heritable characteristics of a population over several generations. These changes can give rise to a new species or the species might change themselves to become better adapted to the surrounding environment.
Origin of Species
- After a successful expedition on HMS Beagle, Charles Darwin wrote a book on what he observed on the Galapagos Islands.
- In the book named ‘The Origin of Species, he wrote a detailed theory of evolution which was mostly based on Natural Selection.
Origin of Life – Haldane’s Theory
- JBS Haldane was a British Scientist who theorized that life originated from organic and lifeless matter.
- His theory was proved to be correct by Urey and Miller’s experiment.
- It was called the theory of abiogenesis.
Evolutionary Evidence – Fossils
- There are plenty of pieces of evidence to support the theory of evolution.
- Fossils happen to be the biggest of them.
- Fossils are the preserved remains of ancient animals or plants that died millions of years ago.
- The fossils help us understand the anatomy and even physiology of these organisms and understand how evolution worked and led to the formation of organisms that we see today.
Formation of Fossils
Fossils are important pieces of evolutionary evidence and are formed by the following steps:
- Organisms die, and they get buried in mud and silt.
- The soft tissues of the body get quickly leave behind the hard bones or shells
- Over time sediments build over it and harden into rock
- As the bones decay, minerals seep in to replace the contents cell by cell, a process called petrification
- If bones decay completely, it leaves behind the cast of the animal.
Evolutionary Relationships
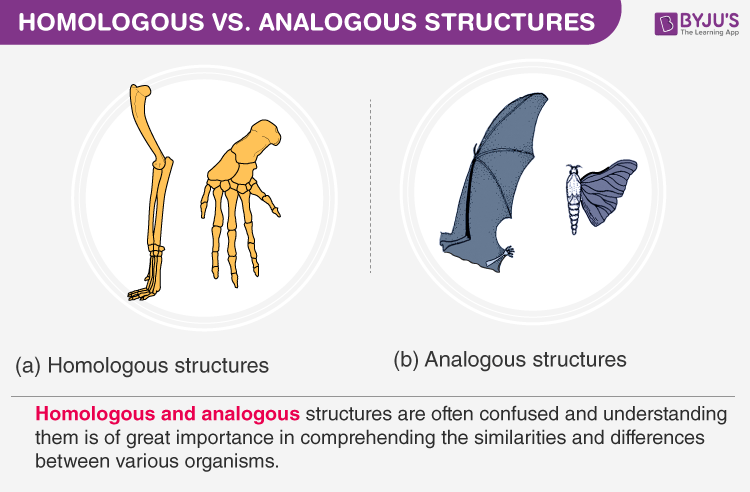
Evolutionary relationships of animals can be deduced by studying the homologous organs and analogous organs.
Homologous organs are those which have a similar structure but different function
- Wings of birds and forelimbs of mammals: have similar structures but are modified to suit different functions.
- A tendril of the pea plant and spine of the barberry plant: both are modified leaves but perform different functions.
Analogous organs are those which have a similar function but a different structure and origin too
- Wings of bats, birds and wings of insects: both are used for flying, but structurally are very different.
- Leaves of opuntia and peepal: both perform photosynthesis, but leaves of Opuntia are modified stems, whereas peepal leaves are normal leaves.
Evolution by Stage
- Evolution is a slow process and does not happen overnight.
- There are several stages in the evolution of almost every animal that we see today.
- Complexities do not evolve suddenly but evolve bit by bit and may have limited use at certain stages.
- This gradual evolutionary process is called evolution by stages.
Artificial Selection
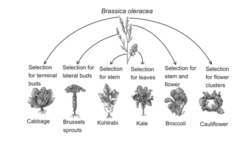
- Sometimes a single species can evolve into several different species due to artificial selection.
- E.g. the cabbage family. A single ancestor in the cabbage family gave rise to several different species due to the selection of different traits.
Molecular Phylogeny
- The evolutionary relationship among different biological species is called phylogeny.
- It gives rise to an evolutionary tree.
- In molecular phylogeny, these relationships are studied at the hereditary molecular level, mainly using DNA sequences.
- It involves the analysis of DNA composition and gene comparison between different species.
Human Evolution
- Humans are known to belong to the primate family.
- Humans today have a very close genetic connection to chimps and other primates.
- While the complete evolutionary process of Humans from Primates is still a mystery, a larger picture of human evolution has been formed.
- Some of the ancestors of Humans include Dryopithecus, Ramapithecus, Australopithecus, Homo erectus, Homo sapiens neanderthalensis, Cro-magnon man, and finally, us, the Homo sapiens.






0 Comments