Introduction
Heredity refers to the passing of characteristics from one generation to the next.
Heredity is normally defined as the method by which an offspring acquires predisposed characteristics from its parent cell. It is the process of transferring genetic traits from parents to their offspring and is initiated by the recombination and segregation of genes during cell division and fertilization.
The process of heredity is the sum of all biological processes resulting in the genesis of a new organism similar to its kind and displaying certain modifications arising from the genes and their interactions with their surroundings.
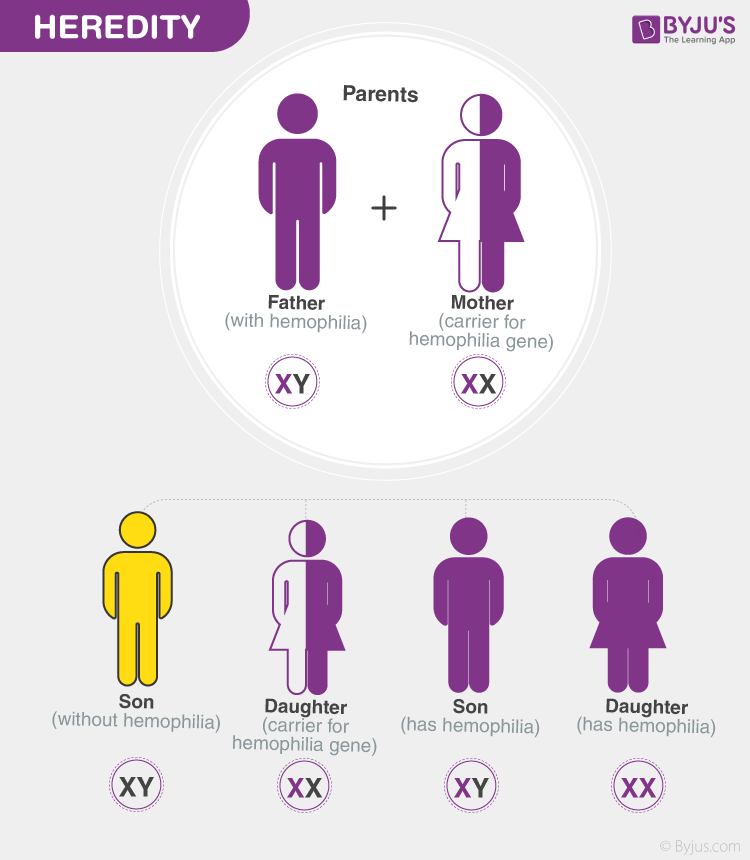
Inheritance
Inheritance works differently during sexual and asexual reproduction.
For example – When one individual bacterium divides, it produces two bacteria which again divides and produce four individual bacterium. The newly generated individuals would be very much similar to each other and there would be only minor differences between them due to small errors in DNA copying. This is the case with asexual reproduction.
In the case of sexual reproduction, greater variation between individuals can be observed. Not all these changes in a species have similar possibilities of surviving in the environment. Their possibilities mainly depend on the nature of variations or evolution. Different individuals have different kinds of advantages.
For example – Drosophila which has a strong resistance to heat will persist better even in a heatwave. So here the selection of variants by environmental factors determines the source of the evolutionary process. Although, several obvious consequences of the reproductive process still remain with the generation of individuals, the similar pattern and the rules of heredity determine the process by which traits and characteristics are reliably inherited.In Biology, inheritance pertains to the transfer of traits from one generation to another.
Heredity
The process by which the features of an organism are passed on from one generation to another is called heredity.
The transfer of traits from one generation to the next is termed heredity. Genes are the functional units of heredity that transfer characteristics from parents to offspring. Genes are short stretches of DNA that code for a specific protein or RNA.
Genetics is the branch of biology that deals with the study of genes, heredity and variations.
Genes
- Gene is the functional unit of heredity.
- Every gene controls one or several particular characteristic features in living organisms.
- The process is done by genes, which define the characters in the organism.
Mendel’s Work
- Gregor Johann Mendel, known as the ‘Father of Genetics’, was an Austrian Monk who worked on pea plants to understand the concept of heredity.
- His work laid the foundation of modern genetics.
- He made three basic laws of inheritance – The Law of Dominance, The Law of Segregation and The Law of Independent Assortment.
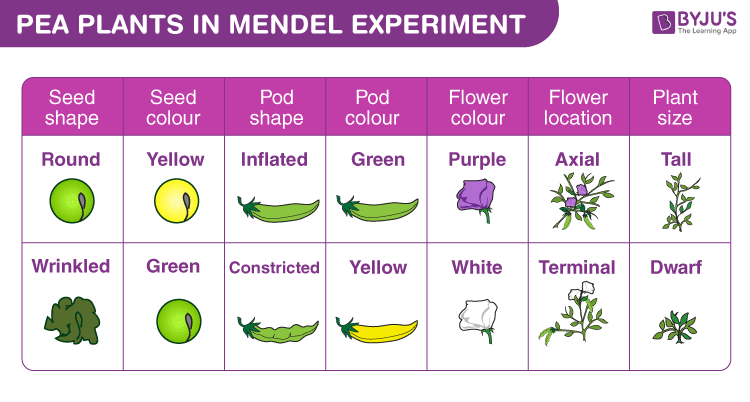
Traits
Traits are characteristic features of an organism, manifested in a physical form that is visible or in a physiological aspect of the organism.
Traits are characteristic features of an organism, manifested in a physical form that is visible or in a physiological aspect of the organism.
Dominant Traits
The traits that express themselves in an organism in every possible combination and can be seen are called Dominant traits.
- In Mendel’s experiment, we see that the tall trait in pea plants tends to express more than the short trait.
- Therefore, the tall trait of the plant is said to be dominant over the short trait.
Recessive Traits
A trait which is not expressed in the presence of a dominant allele is known as recessive.
- So, a recessive character/trait is present in an organism but cannot be seen if a dominant allele exists.
Acquired Characters
- The traits that are acquired by an organism over the period of its lifetime are termed acquired characteristics.
- These characteristics that are not passed on to the DNA of germ cells do not get transferred to the next generation. E.g. loss of muscles and less weight due to starvation, loss of limb or tails due to injury, etc.
Inherited Characters
- The traits that are inherited from the parents are called inherited characters.
- These traits always get transferred to the next generation but depending on the dominance or recessiveness, they may or may not be expressed.
- Examples are height, skin colour and eye colour.
Variation
Variation is the measure of the difference between individuals of the same species. Offspring is not identical to parents, there exist some variations. Each individual in a population differs from the others. Recombination and mutation are the main causes of variations.
Sexually reproducing organisms show great variation among individuals of a species and the long-term accumulation of variations plays a significant role in evolution. The selection of variants by environmental factors is one of the driving factors of evolutionary processes.
Genetic Variations
The differences in the DNA sequences among every organism leading to the diverse gene pool are called genetic variations. These differences lead to different/varied physical characters or biochemical pathways.
Natural Selection
- It is the phenomenon by which a favourable trait in a population of a species is selected.
- Changing natural conditions exert equal pressure on all the existing species.
- The species/organisms which are better adapted to the changing conditions survive and reproduce i.e. selected by nature and species/organisms which cannot adapt perish i.e. rejected by nature.
Speciation
Genetic Drift
Natural selection can play an important role in deciding the traits that survive in a population. However, random fluctuations in gene variants are seen on many occasions. This phenomenon is known as genetic drift. Thus, genetic drift is a change in the frequency of an existing allele in a small population.
Genetic drift may cause a gene variant to disappear from the population and thus reduce genetic variation.
Speciation
It is the process of formation of a new species from existing ones due to several evolutionary forces like genetic drift, isolation of populations, natural selection, etc. Speciation leads to diversity in the ecosystem and the diversity and diversity lead to evolution.
Gene Flow
Gene flow is the transfer of genes from one population to the next. This occurs due to migration or the introduction of organisms to a new population. This results in the change in gene frequencies of a population (A population is a community or a group of animals, plants or any living organism that can reproduce with each other and have fertile, viable offspring).






0 Comments