Overview
Reproduction can be defined as the biological process of producing a new individual or an offspring identical to the parents. This process ensures the increase in the number of individuals of a species when conditions are favourable. It is one of the fundamental characteristics of living things and an essential life process.
There are two types of reproduction – asexual and sexual.
Sexual Reproduction –This process of reproduction is very complex that involves the formation and transfer of gametes, followed by fertilization, the formation of the zygote, and embryogenesis.
Asexual Reproduction — This process of reproduction involves only one parent and the new offspring produced is genetically similar to the parent.
Reproduction in Human Beings
All human beings undergo a sexual mode of reproduction. In this process, two parents are involved in producing a new individual. Offspring are produced by the fusion of gametes (sex cells) from each parent. Hence, the newly formed individual will be different from parents, both genetically and physically. Human reproduction is an example of sexual reproduction.
In human beings, both males and females have different reproductive systems; hence, they are known to exhibit sexual dimorphism. Males have testes- also called testicles, while the females have a pair of ovaries.
Human Reproductive System
The reproduction in human beings involves the fusion of male and female gametes produced in their reproductive system. The male reproductive system is different from the female reproductive system, both in structure and in function.
Male Reproductive System
The male gametes, i.e., sperms are produced within the male reproductive system. Sperms are small unicellular structures with a head, middle piece, and a tail.
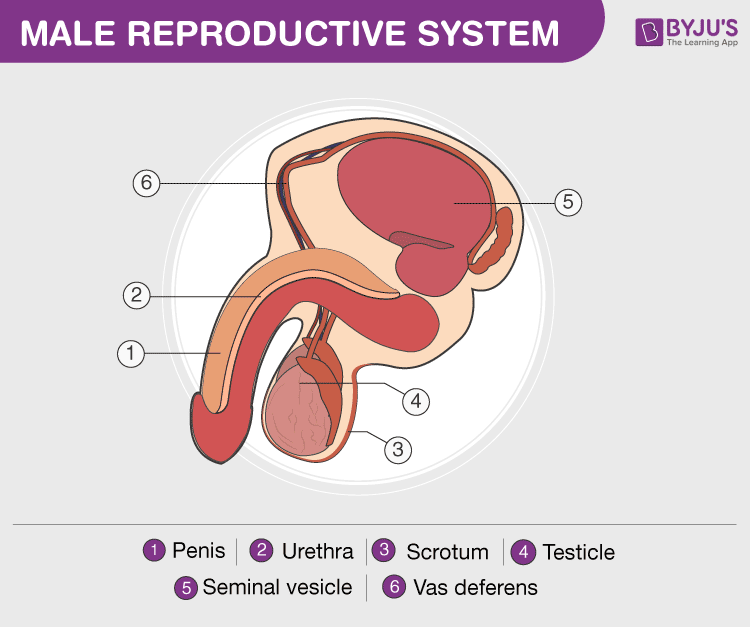
The male reproductive system consists of :
- Testicles (testes): A pair of oval-shaped organs masked in a pouch called the scrotum. They are responsible for the production of sperms and the male hormone testosterone.
- Scrotum: It is a sac-like organ that hangs below the penis and behind it. It is the houses of the testicles, or testes, and maintains a temperature that is required for the production of sperm by it.
- Vas deferens: The sperms produced in testes are stored in a tube called the epididymis. Here the sperms get matured and pass to urethra through the muscular tube called vas deferens.
- Accessory glands: This includes three glands, namely seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and Cowper’s gland. The secretions from the three glands mix to form a fluid called semen. Semen nourishes the sperm, increases the volume and helps in lubrication.
- Penis: Penis is a cylindrical tube which serves as both reproductive organ and an excretory organ. It delivers sperms into the vagina during sexual intercourse.
Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system is active before, during and after fertilization as well. It consists of the following parts:
- A pair of ovaries: Ovaries produce and store ovum in them. They also produce a female hormone called estrogen.
- Fallopian tubes (Oviducts): They are the site of fertilization. They connect ovaries with the uterus.
- Uterus: Uterus is the site of development for the embryo.
- Vagina: It is the part which connects the cervix to the external female body parts. It is the route for the penis during coitus as well as a fetus during delivery.
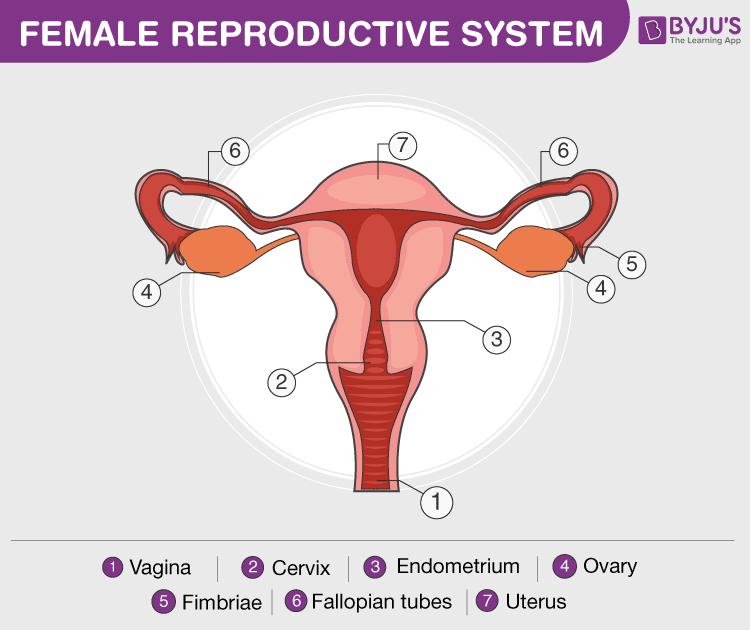
Female reproductive system has two functions –
- Production of female gamete called ovum/egg.
- Providing nutrition and protecting the developing embryo.
During puberty, eggs in the ovaries start to mature. One of the ovaries releases the matured ovum in every 28 to 30 days and is called ovulation.
Reproduction Process in Human Beings
The process of fusion of sperm with egg (ovum) to produce zygote is called fertilization. Fertilization is a crucial stage of reproduction in human beings. The fertilized egg is called the zygote. Zygote starts to divide into many cells and develops into an embryo.
Embryo moves into the uterus and gets attached to its walls. This process is referred to as implantation, and the implanted embryo eventually develops into a fetus.






0 Comments