Land Resources
Land is a natural resource of utmost importance. It supports natural vegetation, wildlife, human life, economic activities, transport and communication systems. India has land under a variety of relief features, namely; mountains, plateaus, plains and islands as shown below:
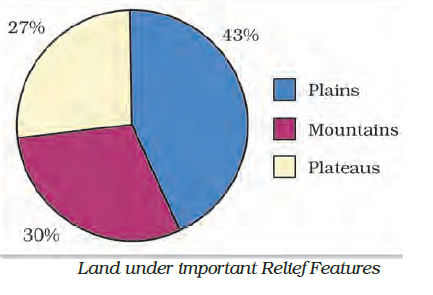
Land Utilisation
Land resources are used for the following purposes:
- Forests
- Land not available for cultivation
a) Barren and wasteland
b) Land put to non-agricultural uses
- Fallow lands
- Other uncultivated lands (excluding fallow land)
- Net sown area
Land Use Pattern in India
The use of land is determined
- Physical factors: such as topography, climate, soil types
- Human factors: such as population density, technological capability and culture and traditions etc.
The data below represents the land use pattern in India.
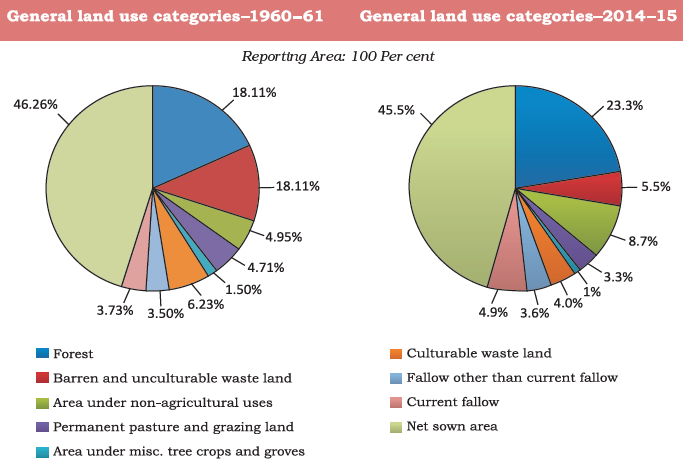
Waste land is the land put to other non-agricultural uses which include rocky, arid and desert areas, roads, railways, industry etc. Continuous use of land over a long period of time without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage it, has resulted in land degradation.
Land Degradation and Conservation Measures
Human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, mining and quarrying have contributed significantly to land degradation. Mining sites leave deep scars and traces of overburdening the land. In recent years, industrial effluents as waste have become a major source of land and water pollution in many parts of the country.
Some of the ways through which we can solve the problems of land degradation are:
- Afforestation and proper management of grazing.
- Planting of shelter belts of plants.
- Stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes.
- Proper management of wastelands.
- Control of mining activities.
- Proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment.






0 Comments