What is Metabolism?
“Metabolism refers to a series of chemical reactions that occur in a living organism to sustain life.”
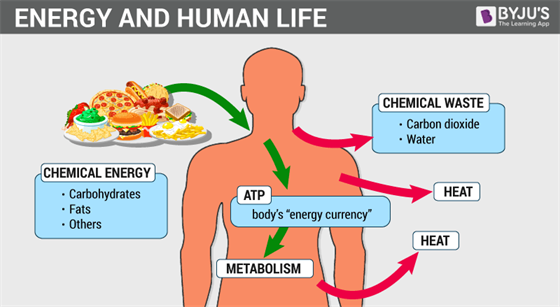
Metabolism is the total amount of the biochemical reactions involved in maintaining the living condition of the cells in an organism. All living organisms require energy for different essential processes and for producing new organic substances.
The metabolic processes help in growth and reproduction and help in maintaining the structures of living organisms. The organisms respond to the surrounding environment due to metabolic activities. All the chemical reactions occurring in the living organisms from digestion to transportation of substances from cell to cell require energy.
Metabolic Process
There are two types of metabolic process:
- Catabolism
- Anabolism
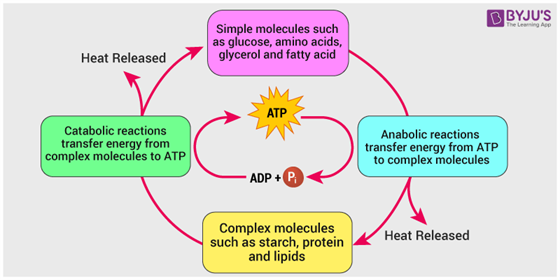
Catabolism – This process is mainly involved in breaking down larger organic molecules into smaller molecules. This metabolic process releases energy.
Anabolism – This process is mainly involved in building up or synthesizing compounds from simpler substances required by the cells. This metabolic process requires and stores energy.
Metabolism is related to nutrition and the existence of nutrients. Bioenergetics describes the metabolism as the biochemical pathway through which the cells obtain energy. One of the major aspects is the energy formation.
Nutrition and Energy
The processes of metabolism depend on the nutrients that get digested to produce energy. This energy is necessary to synthesize nucleic acids, proteins and other biomolecules in our body.
Encompassed nutrients include various substances for the body requirements which are either in the sufficient amount or insufficient, resulting in poor health, concerning metabolism.
Necessary nutrients help by supplying the required energy and other necessary chemicals that the body cannot synthesize on its own. Food provides different substances that are essential for the bodybuilding and repairing of tissues along with the proper functioning of the body.
The diet requires both organic nutrients and inorganic chemical compounds.
Organic nutrients include fats, vitamins, carbohydrates, and proteins.
Inorganic chemical compounds include oxygen, water, and other dietary minerals.
Carbohydrates in Metabolism
Carbohydrates are supplied in three forms:
- Starch
- Sugar
- Cellulose
Starch and sugar are the major forms of energy for humans. Metabolism of carbohydrates and sugar helps in the production of glucose.
Proteins in Metabolism
Proteins are important for building tissues. They help in maintaining the structure of the cells, its functions, the formation of haemoglobin, and several other body functions. The amino acids of proteins are beneficial for nutrition. Few amino acids are not synthesized by the body and are taken in from the food we eat. These amino acids include:
- Lysine
- Tryptophan
- Methionine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Phenylalanine
- Valine
- Threonine
How to Increase Metabolism?
Metabolism can be increased by:
- To be fit and healthy, we need to avoid more calories intake and lose extra pounds. We eat to deliver energy for our body to perform its functions. Eating too little quantities could slow down our metabolism and body cannot provide essential minerals. As per the research, extreme dieting leads to weight loss which is muscle mass and not fat mass.
- Having proper breakfast, boost up the body’s metabolism and keeps us energetic throughout the day. Skipping morning breakfast are more likely to have poor metabolic energy.
- Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system and can activate our metabolism rate by 5 to 8 percent.
- According to researchers, fibre can help in burning fat by 30 percent. People who include more fibre in their diet remain fit and healthy.
- Including more organic foods like peaches, bell peppers, celery, apples, lettuce, grapes can boost up the metabolism rate in our body.






0 Comments