Introduction to Microbiology
Microbiology is the study of a variety of living organisms which are invisible to the naked eye like bacteria and fungi and many other microscopic organisms. Although tiny in size these organisms form the basis for all life on earth. These microbes are also known to produce the soil in which plants grow and fix the atmospheric gases that both plants and animals use. About 3 billion years ago at the time of the formation of the earth, microbes were the only lives on earth. Microorganisms have played a key role in the evolution of the planet earth. The history and scope of microbiology is a diverse topic which will be discussed later in detail.
Microorganisms affect animals, the environment, the food supply and also the healthcare industry. There are many different areas of microbiology including environmental, veterinary, food, pharmaceutical and medical microbiology, which is the most prominent.
Microorganisms are very important to the environment, human health and the economy. Few have immense beneficial effects without which we could not exist. Others are really harmful, and our effort to overcome their effects tests our understanding and skills. The uses of microbiology can be beneficial or harmful depending on what we require from them.
Harmful Microorganisms
Disease and decay are neither inherent properties of organic objects, nor are caused by physical damage, it is microorganisms that bring about these changes. We are surrounded by bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Many microorganisms cause diseases in cattle, crops and others are known for entering human bodies and causing various diseases.
Examples of familiar human diseases are:
Bacteria: pneumonia, bacterial dysentery, diphtheria, bubonic plague, meningitis, typhoid, cholera, salmonella, meningococcal
Virus: Chickenpox, measles, mumps, German measles, colds, warts, cold sores, influenza
Protozoa: amoebic dysentery, malaria,
Fungi: ringworm, athlete’s foot
Useful Microorganisms
As decomposers, bacteria and fungi play an important role in an ecosystem. They break down dead or waste organic matter and release inorganic molecules. Green plants take these nutrients which are in turn consumed by animals, and the products of these plants and animals are again broken down by decomposers.
Yeast is a single-celled fungus that lives naturally on the surface of the fruit. It is economically important in bread-making and brewing beer and also in the making of yoghurt.
Most microorganisms are unicellular; if they are multicellular, they lack highly differentiated tissues.
There are fundamentally two different types of cells, One being Prokaryotic and the other Eukaryotic
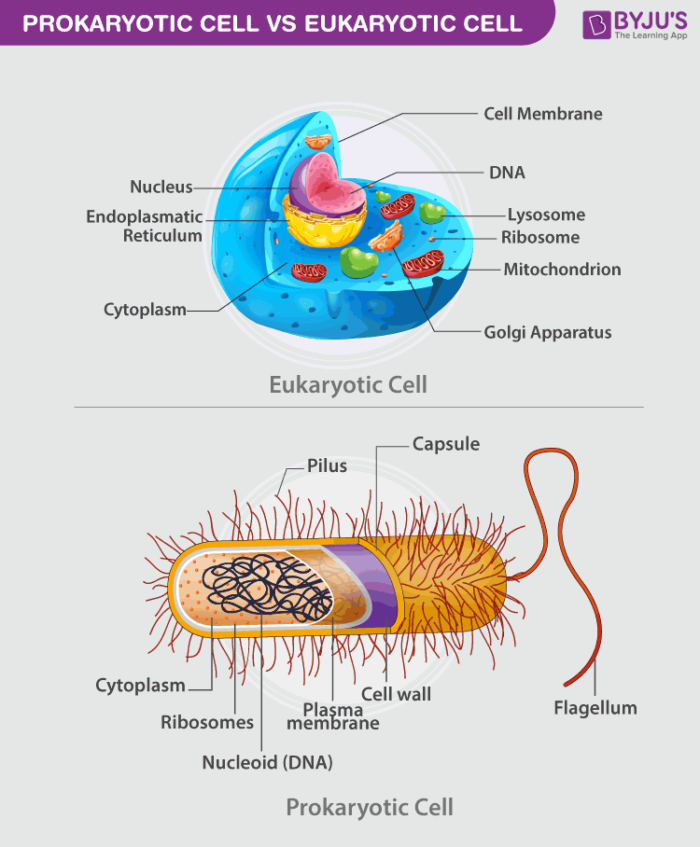
Microbes especially prokaryotes are numerous in number in comparison to eukaryotes.
The lineage of life on Earth originated from these microbes:
1. Bacteria
2. Archaea
3. Eucarya
Branches of Microbiology
There are various different branches of microbiology and these include the following:
1. Bacteriology- The study of bacteria
2. Mycology –The study of fungi
3. Phycology- The study of photosynthetic eukaryotes. (Algae- Seaweed)
4. Protozoology – The study of protozoa (Single-celled eukaryotes)
5. Virology- The study of viruses, non-cellular particles which parasitize cells.
6. Parasitology- The study of parasites which include pathogenic protozoa certain insects and helminth worms.
7. Nematology- The study of nematodes.








0 Comments