Everything that exists in the earth is a form of a matter which is further defined as any substance that occupies space and has mass. The matter is further divided into various forms such as solid, liquid and gas. Apart from these, it is also classified as pure substances and mixtures.
We will learn about the latter in this article.
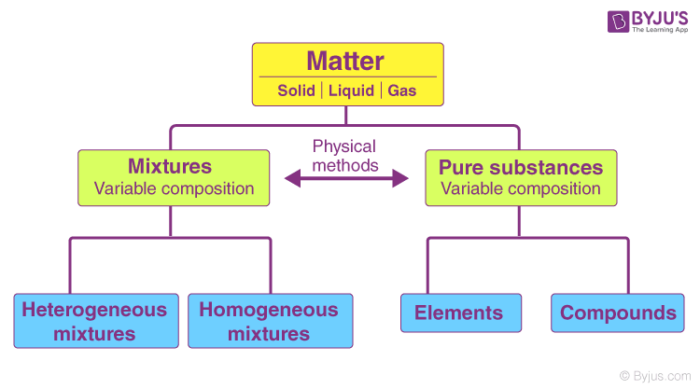
Classification of Matter – Pure Substances and Mixtures
What is Pure Substance?
Pure substances are substances that are made up of only one kind of particle and have a fixed or constant structure.
Pure substances are further classified as elements and compounds.
An element is a substance that consists of only one type or kind of atom. An element is a pure substance as it cannot be broken down or transformed into a new substance even by using some physical or chemical means. Elements are mostly metals, non-metals or metalloids.
Compounds, on the other hand, are also pure substances when two or more elements are combined chemically in a fixed ratio. However, these substances can be broken down into separate elements by chemical methods.
Characteristics and Properties Of Pure Substances
- Pure substances are mostly homogeneous in nature containing only one type of atom or molecule.
- These substances mainly have a constant or uniform composition throughout.
- The substances have fixed boiling and melting points.
- A pure substance usually participates in a chemical reaction to form predictable products.
Examples of Pure Substances
All elements are mostly pure substances. A few of them include gold, copper, oxygen, chlorine, diamond, etc. Compounds such as water, salt or crystals, baking soda amongst others are also grouped as pure substances.
What is a Mixture?
A substance, on the other hand, is impure if it consists of different kinds of elements combined physically and not chemically. Impure substances are also called mixtures. Mixtures are further divided into homogenous or heterogeneous mixture.
- A homogeneous mixture occasionally called a solution, is comparatively unvarying in configuration or constant. Every unit of the mixture is like every other unit. For instance, if you liquefy sugar in water and blend it really well, your concoction is essentially the same, no matter where you sample it. This mixture contains two or more chemical substances.
- A heterogeneous mixture is a concoction whose configuration varies from spot to spot within the sample. For example, if you put a little amount of sugar in a vessel, add some sand, and then shake the jar a couple of times, your concoction doesn’t have the same configuration all throughout the jar. As the sand is heftier, there’s possibly more amount of sand at the bottom of the jar and more sugar at the top part. These mixtures can be identified visually and separated easily by physical means.
Characteristics And Properties Of Mixtures Or Impure Substance
- It does not have any specific properties, the properties of the mixture are a result of the average properties of all the constituents.
- It is formed as a result of a physical change.
- They have a variable composition.
- Their melting and boiling points differ.
Example Of Mixtures
Some common examples of mixtures include;
- Gas and gas like nitrogen and oxygen in the atmosphere.
- A solution like water and oil.
- Gas and liquid such as water.
- Solid and liquid such as sand and water
Differences Between Pure Substances and Mixtures
The differences between pure substances and mixtures are given below.
Physical vs Chemical Changes
The sun rises, the night turns into a day, the seasons change, the leaves shed, flowers bloom and living beings grow! Every day, we see a number of changes happening around us. Change is inevitable. It takes place all the time and everywhere. However, changes differ from one another in a number of aspects. Some changes are fast, others are slow. Some of them are temporary, others are permanent.
Some are periodic, others are non-periodic. Some are natural, others are man-made. Some are reversible, others are irreversible. On the larger front, a change may be categorized into a chemical or a physical change depending on how the properties of a subject alter when it undergoes the change.
Physical Change
A substance is said to undergo a physical change when only the physical properties such as the shape, size, colour, state or appearance of the substance change. Its chemical composition remains intact. Some characteristics of a physical change are:
- Temporary in nature.
- Does not affect the internal structure of a substance, only the molecules are rearranged.
- No new substance is formed.
- Most of the physical changes are reversible. We can obtain the substance back even after the change.

Some examples of a physical change are folding of a paper sheet, melting of wax, freezing and boiling water, melting of ice, condensation, vaporization, magnetizing a compass needle, dissolving sugar in water, etc.
Chemical Change
A substance is said to undergo a chemical change when the chemical properties of a substance alter. As a result, there is either formation or breaking of atomic bonds at the molecular level. Some characteristics of a chemical change are:
- Permanent in nature.
- Since the original composition of the substance changes, one or more new substances are formed.
- Forms of energy, such as heat, light or electricity, may be emitted or absorbed.
- A chemical change is generally irreversible. At least, it cannot be reversed by simple physical means.

Some examples of a chemical change are the burning of paper, burning of fuel, rusting of iron, the souring of milk, growth in a living being, cooking, digestion of food, burning of wood, etc.






0 Comments