Reproduction in Plants
Plants reproduce by both asexual and sexual methods. Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction in plants. Let’s learn now about sexual reproduction in plants.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Sexual reproduction in plants happens through flowers.
- Essential whorls of the flowers such as androecium and gynoecium help in the sexual reproduction of plants.
Non-Essential Parts of Flowers
- The typical structure of flowers contains essential whorls and non-essential whorls.
- Sepals and Petals are called non-essential whorls as they do not directly take part in reproduction.
- Sepals protect the inner delicate whorl during bud condition and also perform photosynthesis if they are green in colour.
- Petals, when they are coloured, attract insects for pollination.
Essential Whorls of Flowers
- Androecium and gynoecium are called essential/reproductive whorls of a flower.
- Androecium produces pollen grains containing male gametes, and gynoecium produces ovules which are female gametes.
- Bisexual flowers contain both whorls, while unisexual flowers contain either of them.
- Each individual member of androecium is called a stamen and consists of an anther and filament.
- Anther produces haploid pollen grains.
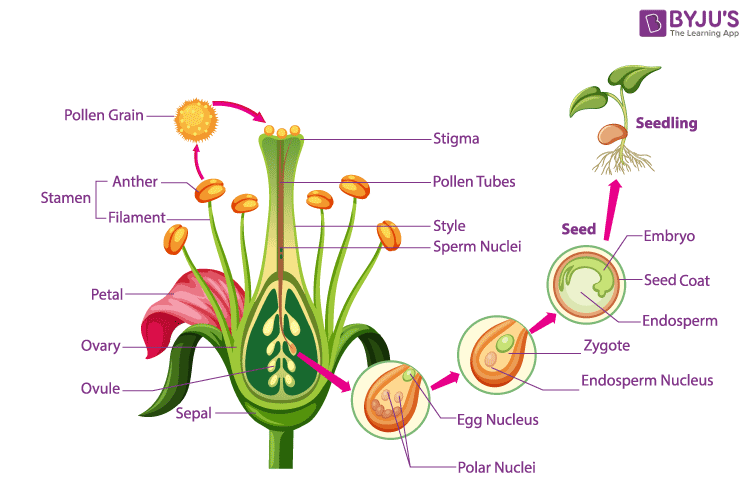
- Each individual member of the gynoecium is called a pistil and consists of a stigma, style and ovary.

Pollination
The process of transfer of pollen grains from anthers to the stigma of a flower is known as pollination.
- It is required for fertilization.
- Pollination has two types, self-pollination (autogamy) and cross-pollination (allogamy).
- In self-pollination, the transfer of pollen grains takes place from anthers to the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same plant.
- In cross-pollination, pollens are transferred from anthers to the stigma of another flower.
- Many pollinating agents play their roles in cross-pollination. Examples: water, wind, insects, birds, bats, etc.
Fertilization
Fusion of male and female gametes is known as fertilization.
- In flowering plants, after pollination, the pollens germinate on the stigma surface of the pistil and generate two male nuclei.
- Ovule has an egg cell and two polar nuclei.
- One male nucleus fuses with two polar nuclei and forms a triploid endosperm.
- Another male nucleus fuses with the egg cell and forms the zygote that gives rise to the embryo and future plant.
- After fertilization, the ovary becomes the fruit, and the ovules turn into seeds. All other parts wither away.






0 Comments